Bias Point Calculation
 View Video
View Video
We will first test the biasing conditions of the circuit AMPLIF.EPB.
1. Right click and select the  Test Points function tool. Select the
Test Points function tool. Select the  Voltage TP to place the testpoints at the base, collector and emitter of the transistor 2N3227.
Voltage TP to place the testpoints at the base, collector and emitter of the transistor 2N3227.
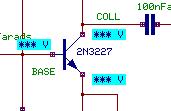
2. All passive component values are seen on the screen. To review the 2N3227 transistor parameters, select function tool  Set parameters/ models and then the
Set parameters/ models and then the  Set Parameter option tool. Click the left mouse button on the transistor to show a dialog box presenting all transistor parameters. These parameters can be modified. Click
CANCEL to exit the dialog box without effecting change and ACCEPT button for the changes to come into effect.
Set Parameter option tool. Click the left mouse button on the transistor to show a dialog box presenting all transistor parameters. These parameters can be modified. Click
CANCEL to exit the dialog box without effecting change and ACCEPT button for the changes to come into effect.
3. We may also use the above step to update the values of any of the passive component in the circuit.
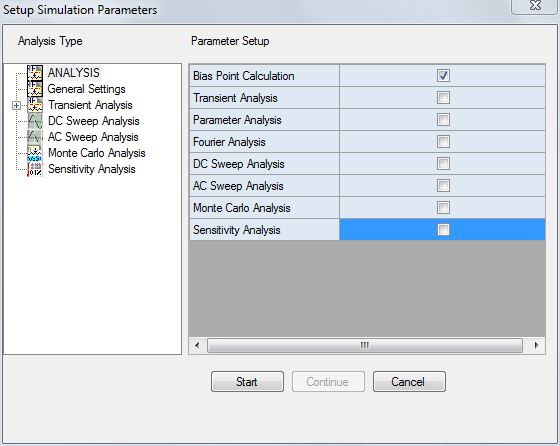
4. After setting the parameters of the circuit, select the Simulation / Analysis menu. A window Setup Simulation Parameters opens with the option Analysis being highlighted on the left side of the window by default. Set the parameters by selecting
GENERAL SETTINGS from the tree view on the left side of the window. Click Accept button to accept the changes and to automatically switch to Analysis option. Check
Bias Point Calculation check box. Now click the START button.
We will observe that the node voltages are displayed at the locations where test points were placed. From this we will observe that the transistor working point is found to be near the saturation region. For more details, we must check its Base and Collector currents. Right click and select  Current TP option tool from the function tool
Current TP option tool from the function tool  Testpoint. Click on transistor base and collector pins to place the Current Testpoint Display Box.
Testpoint. Click on transistor base and collector pins to place the Current Testpoint Display Box.
We will now observe that the transistor is saturated because of: Ib * Beta >> Ic. So set the component parameters such that the Vce voltage is approximately equal to half of the supply voltage. Try to set the value of the resistor RB2 between the transistor Base and ground and then recalculate the Bias Point. To set this value, sweep across a preset range of values in fixed steps and then choose the best value. Simulator provides the DC Sweep analysis function to help us in this.