New features from EDWinXP ver 1.50 to EDWinXP 1.61
What’s new in EDWinXP 1.50
Following release of previous version, several new features and improvement to existing features have been implemented in EDWinXP 1.50
PCB Layout Design and Fabrication
1. Copper pour connectivity test have been added PCB Layout Editor. Similar test was already included in Fabrication Manager. The advantage of this test in Layout Editor is that the connectivity may be checked while the board layout is designed. In both modules, the test may be now performed in selectable accuracy of 0.100, 0.050 and 0.025 mm. The time needed to execute the connectivity test has very significantly reduced.
2. Polygon shapes for copper removal introduced in 1.40, allowed to add feature that automatically removes unnecessary copper in isolated places within copper pour areas. This function was available for 1.40 users through live update. In 1.50, it has been improved in both speed (about 50% reduction of execution time) and accuracy.
3. Gerber View feature has been improved in order to reduce number of selections necessary to pre-process and display artworks in Gerber formats.
4. The option to plot inverted polarity circles and squares in size of pinholes for PMD component and vias has been added for Gerber format output. This option is available for in RS-274-X format only.
5. Settings for all fabrication exports (GenCAM, IDF and newly added Valor’s ODB++ format) have been grouped in common dialog within Fabrication Manager.
6. It is now possible to import projects from other EDA packages in ODB++ format
7. Reconstruction of projects from Gerber format artworks been have significantly improved by adding feature for rebuilding component parts and packages from imported graphics. Projects can be now completely reconstructed even if necessary library elements are not available.
8. Number of tools for automatic routing of connection in PCB Layout Editor has been increased. It is now possible to automatically connect two separate trace branches of a net, re-route connections for a group of relocated components, route lead-out traces from pins of component with complicated pad patterns, automatically miter traces and remove redundant via holes.
9. Online clearance check has been introduced with improved visibility for detected clearance violations.
10. It is now possible to display ratsnest in two modes: will all nodes or with unconnected nodes only.
11. Important function “re-route” trace may be now performed in two modes: “re-route trace segment” and “re-route pin to pin connection. This latter is particularly useful when cleaning up design after auto-routing.
12. Node marker size (squares) and pin entry marker size (crosses) are automatically adjusted to the pitch of component pads in order to ensure best visibility. Similarly, via hole marker size is automatically adjusted to smallest hole diameter in via pad stacks
Schematic Capture and Simulation
1. New feature called Filter Designer has been added. The system library includes prototype circuits for active low-pass, high-pass, band-pass and band-stop filters. Filter Designer allows to select one of the variants of those filters (Chebyshev, Butterworth, Bessel, Elliptic (Cauer) or Universal) and specify required filter output parameters – frequency and quality range. The parameters (capacitance and resistance) for filter circuit components are calculated and updated in the circuit, which subsequently may be appended to the project.
2. It is now possible to convert functional descriptions of discrete parts, expressed in form of SPICE format sub-circuit into analogue model for Mixed Mode Simulator.
3. Following code models have been added to MM Simulator and EDSPice model libraries:
4. New feature called Filter Designer has been added. The system library includes prototype circuits for active low-pass, high-pass, band-pass and band-stop filters. Filter Designer allows to select one of the variants of those filters (Chebyshev, Butterworth, Bessel, Elliptic (Cauer) or Universal) and specify required filter output parameters – frequency and quality range. The parameters (capacitance and resistance) for filter circuit components are calculated and updated in the circuit, which subsequently may be appended to the project.
5. It is now possible to convert functional descriptions of discrete parts, expressed in form of SPICE format sub-circuit into analogue model for Mixed Mode Simulator.
6. Following code models have been added to MM Simulator and EDSPice model libraries:
| EDSPICE code models | MM Simulator models |
| M7218CD | DAC0800 |
| Max456 | ADC0800 |
| Max4587 | MAX232 |
| Max522 | DAC AD 569 |
| max5341 | HPDL1414 |
| max5352 | ULN2003A |
| max625 | Stepper Motor |
| max690 | Potentiometer |
| max691 | LCD Display |
| max696 | LCD Display Driver-HD44780U |
| max697 | SweepGenerator.dll |
| max697 | SweepGenerator.dll |
| max701 | |
| max702 | |
| max708 | |
| max7225 | |
| MAX7240 |
7. EDSPICE updates for EDWinXP 1.50
Sub-circuit files
• Diac
• CCCS
• CCVS
Circuit files (SPICE netlist format)
• BUCK CONVERTER AC MODEL.CIR
• DC_MOTOR_MODEL.CIR
• TREBLE AND BASS TONE CONTROLS.CIR
• I-TO-V CONVERTER (TRANSIMPEDANCE AMP).CIR
• CCCS.CIR
Sample projects with new EDSPICE sub-circuits
• 7805 Regulator - voltage regulator 7805
• CENTRE TAPPED TRANSFORMER - transformer
• Controlled Full Wave Rectifier - SCR
• OPTOCOUPLER- OPTOCOUPLER
• IGBT - IGBT
• Sidac characteristics - sidac
• UJT Relaxation Oscillator – UJT
• Current Controlled Current Source - CCCS
• Current Controlled Voltage Source – CCVS
Updates in Part Libraries
| PART | MANUFACTURER | SYMBOL | PACKAGE |
| 0805AS-2N7M-01 | Fastron | INDUCTOR | L/L70/SM |
| 59S101-400E3 | Rosenberger | CONN | CON/F5/A |
| 74HC4052D | Philips | MUX4052 | SOIC16/150 |
| 8516-4500 | 3M Interconnect Solutions | CONN | CON/HEADER16/A |
| 8520-4500 | 3M Interconnect Solutions Division | CONN | CON/HEADER16/A |
| 8526-4500 | 3M Interconnect Solutions Division | CONN | CON/HEADER16/A |
| 8540-4500 | 3M Interconnect Solutions Division | CONN | CON/HEADER16/A |
| 8560-4500 | 3M Interconnect Solutions Division | CONN | CON/HEADER16/A |
| A3953SB | Allegro | DRV3953 | DIP16/300 |
| ACSL-6400-T | Agilent Technologies | OPTO6400 | SOIC16/150 |
| ADF7020BCPZ1 | Analog Devices | TxRx7020 | LCC48/A |
| AT91SAM7S64 | Atmel | MICR91SAM7S | QFP64/D |
| ATmega128L-8MC | Atmel | MICR128 | LCC64 |
| bq24022DRC | Texas Instruments | ADPTR24022 | LCC10 |
| BSP742T | Infineon technologies | SWT742 | SOP8/150 |
| C-551SR | Para Light | DISP5503 | DIP10/600 |
| CY8C27443-24PXI | Cypress | MCNTRLR8C27443 | DIP28/300 |
| DB15SRT/3R | Amphenol | CONN | CON/DB15/D |
| DCP010515DBP-U | Burr-Brown | DCP0105D | DIP14/300/P7 |
| DS1822 | Dallas Semiconductor | THERMO1822 | TO92/3 |
| dsPIC30F5011 | Microchip | CNTRLR30F5011 | QFP64/C |
| dsPIC30F6011 | Microchip | CNTRLR30F6011 | QFP64/C |
| dsPIC30F6014 | Microchip | CNTRLR30F6014 | QFP80/B |
| EP2C8F256 | Altera | FPGA8C256F | BGA256/e40 |
| F3345 | FOX Electronics | XTALOSC1 | DIP4/SM/3 |
| FDC6301N | Fairchild | PFET_DG | SOT23/6 |
| FDV303N | Fairchild | NFET_DG | SOT23/3 |
| FSA4157P6 | Fairchild | SPDT4157 | SC88 |
| G5V-2 | OMRON | RLY1FORMC,RLY1FORM | DIP16R/8 |
| GM5WA06260A | SHARP | LED | DIP6/SM |
| L5973D | ST Micro Electronics | VREG5973 | SOP8/150 |
| L6203 | ST Micro Electronics | DRV6203 | TO220/11 |
| LAN91C111 | SMSC | LAN91C111 | QFP128/C |
| LATBT66C | OSRAM | 3DIODE | DIP4/SM/B |
| LPC2106FBD48 | Philips | MCNTLR2106 | QFP48 |
| LZ-12VM | FUJITSU | RLY1FORMC | DIP5 |
| M54562FP | Mitsubishi | DARARRAY54562 | SOP20/200/A |
| MAX5400EKA-T | Maxim | DPOT5400 | SOT23/8 |
| MAX952ESA | Maxim | AMPR952 | SOIC8/150 |
| MC6802P | Motorola | MICR6802 | DIP40/600 |
| MC6821P | Motorola | ADAPTR6821 | DIP40/600 |
| MCF5235CVM100 | Freescale | MICR5235 | BGA256/e40 |
| MIC2941ABU | Micrel | VREG2941 | TO263/5 |
| MM5450BN | Micrel | DRV5450 | DIP40/600 |
| MMA7260Q | Freescale | ACCLR7260 | QFN16 |
| MSC1202Y2RHHR | Texas Instruments | ADC1202 | LCC36/A |
| nRF905-EVKIT 868/915 | NORDIC | TxRx905 | LCC32/A |
| PIC16F688I/SN | Microchip | MCNTLR16F688 | SOIC14/150 |
| PIC16F876/SO | Microchip | MICR16F873 | SOIC28/300 |
| PIC18F4220-I/P | Microchip | MCNTRLR18F4220 | DIP40/600 |
| PIC18F452-I/P | Microchip | MCNTLR18F442 | DIP40/600 |
| PIC18F452-I/PT | Microchip | MCNTLR18F442 | QFP44/C |
| PIC18F4550 | Microchip | MCNTRLR18F4550 | DIP40/600 |
| PIC18F458-E/L | Microchip | MCNTRLR18F458 | LCC44 |
| QMB-111PC | Star | BUZZER | PMD2/e12 |
| QT1080-ISG | Quantum | SENSOR1080 | LCC32/A |
| RY-12 | FUJITSU | RLY1FORMC,RLY1FORM | DIP16R/8 |
| TA7252AP | Toshiba | AMP7252 | SIP7/A |
| TDA7294V | ST Micro Electronics | AMP7295 | TO220/15 |
| TEL3-2422 | Traco | CONV2422 | DIP14/400/8 |
| TLE5205-2GP | Infineon technologies | BRIDGE5205 | SOP20/425 |
| TLE6228GP | Infineon technologies | SWT6228 | SOP20/425 |
| TLE6232GP | Infineon technologies | SWT6232 | SOP36/400 |
| TLMK330 | Vishay | LED | LCC2 |
| TMP36FS | Analog Devices | SESOR36 | SOIC8/150 |
| UC3906DW | Texas Instruments | ADPTR3906 | SOIC16/300 |
| ULN2004D | ST Micro Electronics | DARARRAY2003 | SOIC16/150 |
| XC9572 | Xilinx | PLD9572 | LCC44 |
| TJA1040 | PHILIPS | CANCNTR1040 | SOIC8/150 |
| LM317AMDT | NATIONAL | ADVOLTREG | TO252/C |
| FT232RL | FTDI Chip | UART232A | SOP28/200 |
| 2SA933AS | Rohm | PNP | TO202/3/B |
| 2SC174S | Rohm | NPN | TO202/3/B |
| HD44780UA00TF | HITACHI | DISPCNTRLR44780 | TQFP80 |
| HD44780UA02TF | HITACHI | DISPCNTRLR44780 | TQFP80 |
Symbol only parts
What is New in EDWinXP 1.60 and EDWinXP 1.61
Project Version Control
Project version control enables storing of different versions of a project in the same disk file. Current version may be saved at any time and all saved versions become part of the same project database. Any saved version may be restored immediately and set as current. Since all recorded versions are included in the same database and are loaded from and stored in a single common disk file, there is no need to keep track of different version files and worrying about backups. It would be enough to back up only one file containing all recorded versions. It also allows to reconstruct single project database with several versions that were stored as separate database files (.epb) in previous versions of EDWinXP. There are provisions to view general and statistics information’s and also to compare selected version with the active version. The new structure of database makes it incompatible with previous version of EDWinXP. Older project are fully upward compatible, can be loaded and will be automatically converted to the new format. There is also possibility to save selected project versions in a separate file in the format accepted by older releases of EDWinXP. Note: This feature is available only for EDWinXP Professional.
Layout Editor
Trace Length and Width TrimmingThis feature allows inserting pattern of segments into selected trace in order to obtain exact specified length. The shape of the pattern, its amplitude and step length may be set as parameters for calculation of necessary number of steps. All user has to do is to select the suitable point in the trace where the pattern should be inserted. This is done interactively – the pattern (generated according to currently set parameters) is visible and follows cursor while it is moved along the trace. Parameters may be adjusted during this time until permanent insertion is confirmed by the mouse click.
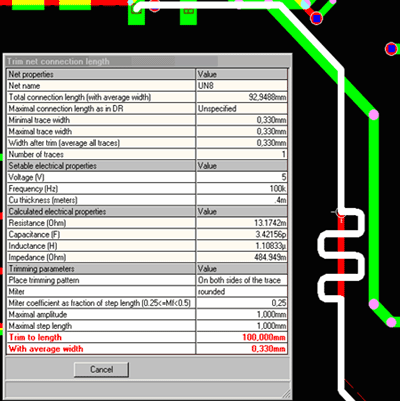 Trimming function works in three modes: trimming single trace to specified length, trimming two traces to the length of longer one and trimming net connection to specified length. In the latter mode, it is possible to see how changing of length and average trace width affects net’s electrical properties (resistance, capacitance, inductance and impedance)
As further requested improvement, the current trace length is dynamically calculated while trace is manually routed or re-routed.
Trimming function works in three modes: trimming single trace to specified length, trimming two traces to the length of longer one and trimming net connection to specified length. In the latter mode, it is possible to see how changing of length and average trace width affects net’s electrical properties (resistance, capacitance, inductance and impedance)
As further requested improvement, the current trace length is dynamically calculated while trace is manually routed or re-routed.
Automatic correction of selected clearance errors
Reporting of clearance errors have been improved by providing additional details of detected conflicts. The dialog presenting locations of conflicts is always visible (modal) while navigating from error to error. Focused errors are distinctly marked for exact identification.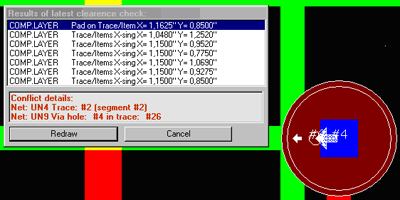 Another new feature is automatic correction of selected clearance error. This function works in two modes. Error to correct may be selected by pointing corresponding marker on the screen. The program is now able to recognize exactly which traces are in conflict. The one that creates most conflicts is automatically rerouted. In other mode, the user may select any of conflicting traces and order its automatic rerouting.
Another new feature is automatic correction of selected clearance error. This function works in two modes. Error to correct may be selected by pointing corresponding marker on the screen. The program is now able to recognize exactly which traces are in conflict. The one that creates most conflicts is automatically rerouted. In other mode, the user may select any of conflicting traces and order its automatic rerouting.
Automatic clearance correction after routing and rerouting
In version 1.61, the on-line clearance check feature has been strongly enhanced by automatic correction of all clearance errors caused by the last route or reroute operation. This function has several options. It may be specified that correction should be executed always when error are detected without asking. Alternatively, information that errors have been detected is displayed awaiting confirmation for executing correction. It is also possible to order that correction should apply to the last routed/rerouted trace or that this trace must be left unchanged and only other conflicting traces should be automatically rerouted.Automatic “trace project” feature
Pressing key combination, Shift A when a trace is manually routed or rerouted activates and deactivates automatic “trace project” function. Following happens, depending on currently executed operation:- When a new trace is created and the function is ON, the program automatically routes clearance error free connection from the last inserted point to current cursor position. Cursor movement changes this so-called “trace project” to reroute dynamically depending on obstacles encountered on the way. Mouse click confirms that trace project to this point is accepted and subsequent trace project starts to be routed from this point. Even if the route suggested by trace project is not accepted, the feature may be used to seek best way for manual routing. It is possible to alternate (by Shift A) between the modes and route some parts of the trace manually and some parts automatically.
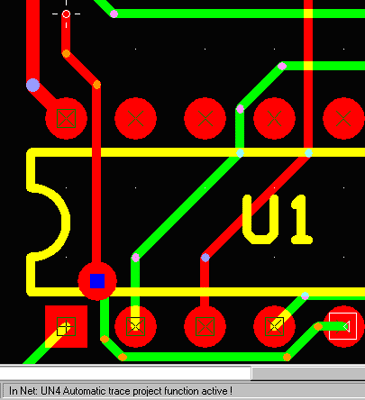
- When a trace point or segment is relocated, and the automatic trace project function is ON, the program reroutes preceding and following segments of the trace, starting in both directions from current cursor position. Using option “rip-up before reroute” allows in this case rerouting of entire connection between two nodes
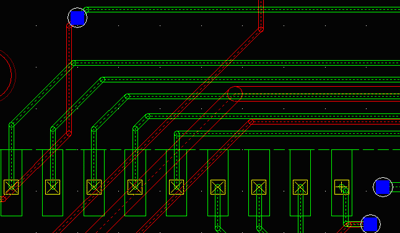
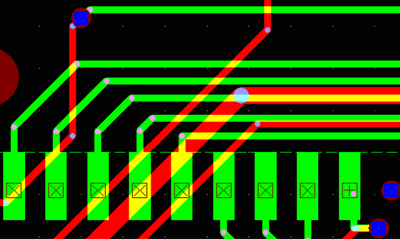 The transparency due to “XORed” trace display is clearly visible on the picture above showing True Size mode view. Trace Frames mode produces in this case small reddish circles representing position of bending points. This feature helps in detecting redundant bending points (inserted often by careless manual routing) that create unnecessary collinear trace segments
According to the same rule, oval pads created from lines of certain length and with are presented in contoured form that allows seeing their real size outlines in Centerline view mode with Pad Frames ON.
The transparency due to “XORed” trace display is clearly visible on the picture above showing True Size mode view. Trace Frames mode produces in this case small reddish circles representing position of bending points. This feature helps in detecting redundant bending points (inserted often by careless manual routing) that create unnecessary collinear trace segments
According to the same rule, oval pads created from lines of certain length and with are presented in contoured form that allows seeing their real size outlines in Centerline view mode with Pad Frames ON.
 On users’ request, Padstack Creation Wizard has been equipped with possibility to create rectangular SMD pads with rounded corners). Other issue connected to padstacks that has been solved in this version is the possibility to create SMD pads on top and bottom layers. Check for connectivity in Layout Editor that did not allow connection of trace to bottom placed pad in a component placed on top layer has been accordingly changed. This especially makes creating of packages representing finger connectors easier and more straightforward.
On users’ request, Padstack Creation Wizard has been equipped with possibility to create rectangular SMD pads with rounded corners). Other issue connected to padstacks that has been solved in this version is the possibility to create SMD pads on top and bottom layers. Check for connectivity in Layout Editor that did not allow connection of trace to bottom placed pad in a component placed on top layer has been accordingly changed. This especially makes creating of packages representing finger connectors easier and more straightforward.
Shortcut to copper check added to flood test in Layout Editor
The flood test for copper pour connectivity that has been implemented in previous version has been enhanced to include also shortcut check. In this manner, all layout design testing functions are finally grouped in one application.More padstacks for via holes
Number of available padstacks for via holes (previously 7) has been increased to 16. To facilitate differentiation among various padstacks, it is now possible to add labels to each of them for individual recognition. It is even possible to highlight vias using given type of padstack.Library Editor
Auto dimensioning of packages and padstacks
Users who produce boards on order often need to document library elements created for each design, even in printed form. For this purpose, dimensioning of packages and padstacks has been implanted in version 1.61. Tables with dimensioning data in following form are created fully automatically after switching to this mode while editing packages in Library Editor or viewing them in Package Viewer: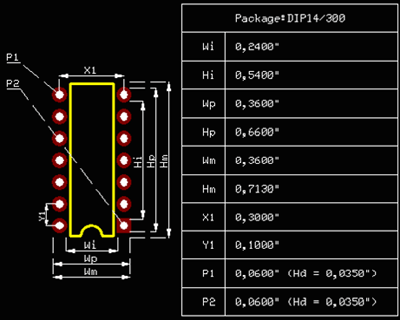
List of Material Editor
This module has been replaced by completely rewritten new version that on one hand allows creating simple lists much easier and on the other allows using advanced feature of External Info Database in more straight forward, intuitive way. Additionally, output filters have been introduced enabling to generate variants of BOMs from the same project database.Fabrication Manager
- Undo/Redo feature is implemented, which is especially needed when reconstructing projects from graphic imports.
- Introduced simple means for aligning images.
- New fabrication export has been implemented, this time for exporting CNC data in G-CODE format containing generic machining program for cutting board outline contours and internal cutouts. Toolpath for cutting are also calculated allowing for specified cutter diameter (cutting outside outer contour and cutting inside internal outlines).
Mixed Mode Simulator
As a complement to previously released development kit for PIC16C family of microcontrollers, with 1.61 we are releasing similar kit for PIC16F84/C84 family containing C-compiler, Assembler, Debugger and instructive application examples. New microcontroller kit and simulation models- New models created in MMI technology for:
- Line 5 x 8 dots LCD display full version
- HD44780U LCD display driver full version
- Line 5 x 8 dots LCD display
- Line 5 x 10 dots LCD display
- Voltmeter (instrumental)
- GLED
- OrLED
- Standard digital models:
- 74F579-8-bit bidirectional binary counter (3-State)
- 74F597-8-bit shift register with input flip-flops
Mouse wheel
Support for mouse wheel has been fully implemented in version 1.60. The wheel is used for zooming graphic display in and out with simultaneous panning to point shown by the cursor. Mouse wheel may be also used to scrolling up and down the tables (grid control) that are displayed in pop up dialogsVista compatible help system
All help files have been converted and re-edited for compatibility with Microsoft Vista operating systemMany small improvements
Many requested small improvements have been added to the system and not all of them are clearly visible. Just to mention a few:- ALT key to initiate entering of shortcut commands. This has been added for improved ergonomics.
- Provision to see total design time in project properties.
- Long cursor feature in wave form viewer.
- List of recently opened projects has been increased to 8 in project explorer's File option.
- Content of data created by List Generator program has been extended to include component values.
- Measurement function recognizes more object types (board outline) and displays not only distance but also delta X and delta Y between measured objects.
- Nodes in Net Property dialog (Schematics Editor) are displayed grouped by schematic pages where they are located.
- Pins numbers in Component Property (Layout Editor) dialog are displayed with corresponding schematic entry names
- Refreshing of elements in Project Library may be done selectively.
- Opening of padstack editor may be done directly from Layout Editor.
- Number of groups that can be added at a time is increased to 128.
LIST OF NEW PARTS UPDATED IN EDWINXP 1.61
| No. | PART | SYMBOL | PACKAGE |
| 1. | 10MQ100N | DIODE | DO214AA/2/L175/B |
| 2. | 1-1740194-2 | CONN | CON/DB9/SMD |
| 3. | 1N4148 | DIODE | SOD80/2/L125/A |
| 4. | 3296W-1-103LF | RESPOT3296 | RTP3 |
| 5. | 4HEADERL/A | CONN | CON/HEADER4/A |
| 6. | 500075-1517 | 500075-1517 | 500075-1517 |
| 7. | 8279 | I8279 | DIP40/600 |
| 8. | A3984SLP-T | DRV3984 | SOP24/170 |
| 9. | A4983SET-T | DRV4983 | LCC28/C |
| 10. | AMP 1-6605834-1 | CONNRJ10 | CON/RJ45-10 |
| 11. | ATmega1281V-8MU | MICR1281 | LCC64 |
| 12. | ATmega128L-8MC | MICR128 | LCC64 |
| 13. | ATmega64L-8MC | MICR128 | LCC64 |
| 14. | ATmega8L-8AC | MCNTLR8L | QFP32 |
| 15. | B6TS-04LT | SNSB6TS | SOP20/150 |
| 16. | C8051F320 | MICR8051320 | QFP32/A |
| 17. | C8051F321 | MICR8051321 | QFN28 |
| 18. | C8051F350-GQ | MICR8051350 | QFP32/A |
| 19. | C8051F351-GM | MICR8051351 | LCC28/C |
| 20. | CC0402 | CAP | C/L105/SM |
| 21. | CC0603 | CAP | C/L171/SM |
| 22. | CD4098BE | MUL4098 | DIP16/300 |
| 23. | CLE-115-01-G-DV3 | CONN | CON30/SMD |
| 24. | CP1A-12V | RLYCP1A-12V | RELAY4 |
| 25. | DM9000E | MACCNTRLR9000 | QFP100 |
| 26. | ELS-511GWA | LCD511 | DIP10/A |
| 27. | eZ80F91AZA50EG | MCNTRLZ809150 | QFP144 |
| 28. | eZ80F91AZA50SG | MCNTRLZ809150 | QFP144 |
| 29. | HCNR200-300E | OPTO200 | SOIC8/350 |
| 30. | HCPL-7800A-300E | AMP7800 | SOIC8/250 |
| 31. | HEF4049BT | INV | SOIC16/150 |
| 32. | HEXFET7507 | HEXFET7507 | MICRO8 |
| 33. | INA196AIDBV | MON196 | SOT23/5/A |
| 34. | IRF7507PbF | MOSFET7507 | MICRO8 |
| 35. | IRFR2407 | MOSFET 2407 | TO252/2 |
| 36. | KLBR4 | CONN | CON4 |
| 37. | L6229D | DRV6229 | SOIC24/300 |
| 38. | LM2937-3-3 | REG2937 | SOT223/4 |
| 39. | LM2937IMP | REG2937 | SOT223/4 |
| 40. | LM3940IMP-33 | VOLTREG | SOT223/4 |
| 41. | LP2960IM-50 | VOLTREG2960 | SOIC16/150 |
| 42. | LPC2212FBD144 | MICR2212 | QFP144/C |
| 43. | LPC2212FBD144/00RT | MICR2212 | QFP144/C |
| 44. | LPC2214FBD144 | MICR2212 | QFP144/C |
| 45. | LPC2214FBD144/00 | MICR2212 | QFP144/C |
| 46. | MAX1241BCPA | ADC1241BCPA | DIP8/300 |
| 47. | MAX232CPE | TxRx232 | DIP16/300 |
| 48. | MAX7301AAI | INTRF7301/A | SOP28/200 |
| 49. | MC68HC812A4CPV8 | MICR68812 | QFP112 |
| 50. | MIC24011-0101T-LF3 | TRANSMR24011 | TFR12/RJ45 |
| 51. | MiniDimm200_FCI59355 | FINGER | 59355 |
| 52. | MMA7260QT | ACCLR7260 | QFN16 |
| 53. | MMC73-105K50K37-TR12 | CAP | C/L750/SM |
| 54. | MRF24J40 | TRANS2440 | QFN40 |
| 55. | NEB/J25R | CONN | CON/PWR3/J25R |
| 56. | P89C51RD2BBD/01 | i8051/A | QFP44 |
| 57. | PIC16F876/SP | MICR16F873 | DIP28/300 |
| 58. | PIC18F4620 | MICR18F4620 | QFN44 |
| 59. | PWRCON3 | CONN | CON/PWR3/B |
| 60. | PWRCON3/A | CONN | CON/PWR3/A |
| 61. | RW0S6BBR010FE | RES | SMD2010 |
| 62. | SN75451B | DRV75451 | SOIC8/150 |
| 63. | SP485CN | TXRX485 | SOIC8/150 |
| 64. | STR710FZ1T6 | MCU71x | QFP144/C |
| 65. | STR710FZ2T6 | MCU71x | QFP144/C |
| 66. | STR710FZT6 | MCU71x | QFP144/C |
| 67. | TDA8945S | AMP8945 | SIL9P |
| 68. | TPMEXXXK | CAP | L/L295/SM |
| 69. | UDN2981A-T | DRV2981 | DIP18/300 |
| 70. | UDN2982A-T | DRV2981 | DIP18/300 |
| 71. | Z80 | MCNTRLZ80 | QFP44C |